D electron pair acceptor. Reagents that seek to react with a proton or some other electron-deficient center are called _____.

Wcln The Bronsted Lowry Theory Of Acids Chemistry Youtube
Highlight the limitations of Arrhenious and Bronsted.

. Hereof what is an acid according to Bronsted Lowry. HCl aq H 2 O l H 3 O aq Cl aq - III. According to Bronsted-Lowry theory a base is defined as a.
An acid and a base react to form a conjugated base. According to the Bronsted-Lowry theory an acid is any substance molecule or ion that can transfer a proton H- ion to another substance and a base is any substance that can accept a proton. A base is defined as a substance which accepts protons and forms conjugate acid.
Its conjugate acid is NH4. According to the Bronsted-Lowry conjugate acid-base theory. Bronsted lowry acids and bases worksheet answers.
According to Bronsted Lowry theory acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors. Find out how to identify the Brønsted-Lowry acid and base in a reaction and recognize the conjugate partner of each. According to Bronsted-Lowry theory an acid is a substance that can _____.
In reaction I the reaction between hydrochloric acid HCl and ammonia is taking place in aqueous solution. This theory is a. According to which Donor of proton is acid where as acceptor of proton is base.
When it donates its proton the acid becomes its conjugate base. In contrast a Bronsted-Lowry base accepts hydrogen ions. According to Bronsted-Lowry theory an acid is a proton H1 donor and a base is a proton acceptor.
E The primary ingredient in Drano is sodium hydroxide. A substance containing OH-ions. An acid is a substance which donates protons.
According to Bonsted-Lowry an acid is a compound that donates a Hydrogen ion or proton to form a conjugate base In the Bronsted-Lowry theory what does an acid do. When it donates its proton the acid becomes its conjugate base. A Bronsted-Lowry acid is a chemical species that donates one or more hydrogen ions in a reaction.
A base is a substance which accepts protons. If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website. According to Bronsted-Lowry theory an acid is a substance which can donate a proton while base is a substance which can accept a proton.
Another theory is bronsted lowry theory which is a Proton Donor acceptor concept. A Bronsted-Lowry acid is a chemical species that donates one or more hydrogen ions in a reaction. A more general look at the theory is an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton.
An acid is defined as a substance which looses or donates protons and forms conjugate base. Acid Conjugate base. The Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory or Bronsted Lowry theory identifies strong and weak acids and bases based on whether the species accepts or donates protons or H.
Acid-base reactions are proton- transfer reactions as follows. According to Bronsted-Lowry theory substances that act as proton donors are called acids while those who accept protons are called bases. The molecule or ion that is formed when an acid loses its proton is called the _____.
D Arrhenius bases are also called hydroxide bases. According to Bronsted Lowry theory acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors. C Dissociation is the process by which Arrhenius acids produce H ions in solution.
According to Lewis theory a base is a substance that can _____. Label the Bronsted-Lowry acids A bases B conjugate acids CA and conjugate bases CB in the. According to the Bronsted-Lowry theory a base is a n.
The BrønstedLowry theory is an acidbase reaction theory which was proposed independently by Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and Thomas Martin Lowry in 1923. Define acids and bases based on the Bronsted Lowry concept. Base Conjugate acid.
HA B. In contrast a Bronsted-Lowry base accepts hydrogen ions. Label the Bronsted-Lowry acids A bases B conjugate acids CA and conjugate bases CB in the.
D The acid found in car batteries is sulfuric acid. B In the pure state Arrhenius bases are ionic compounds. C electron pair donor.
The fundamental concept of this theory is that when an acid and a base react with each other the acid forms its conjugate base and the base forms its conjugate acid by exchange of a proton. In terms of acid strength which pair are ranked INCORRECTLY. According to the question the correct answer is a base is a proton acceptor.
I NH3 is a Bronsted base because it can accept a proton. BRONSTED - LOWRY ACIDS BASES WORKSHEET According to Bronsted-Lowry theory an acid is a proton H1 donor and a base is a proton acceptor. For example-H C l H C l HCl is donating a proton in the aqueous medium.
In an aqueous state HCl first reacts with H 2 O. Its conjugate base in NH2-. BRONSTED - LOWRY ACIDS BASES WORKSHEET According to Bronsted-Lowry theory an acid is a proton H1 donor and a base is a proton acceptor.
According to Arrhenius theory substance which can give H Ion when dissolved in water is acid and a substance which can give OH- ions when dissolved in water is known as base. A In the pure state Arrhenius acids are covalent compounds. A more general look at the theory is an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor.
Unit 14 Acids Bases 1 Worksheets Reg. NH3 is also a Bronsted acid because it can donate a proton. For example-H C l H C l HCl is donating a proton in the aqueous medium.
Learn about the Brønsted-Lowry definition of acids and bases. Showing top 8 worksheets in the category - Bronsted Lowery. Acids And Bases Worksheet 2 Worksheet Bronsted lowry acids and bases worksheet answer key.
A base accepts a proton to form a conjugate acid. In the above reaction there is a proton transfer between hydrochloric acid and water to form the hydronium ion and loses a proton to form chloride ion. According to the theory an acid and base react with each other causing the acid to form its conjugate base and the base to form its conjugate acid by exchanging a proton.
Bronsted Lowery Worksheets - Kiddy Math Bronsted Lowery. Brønsted-Lowry theory also called proton theory of acids and bases a theory introduced independently in 1923 by the Danish chemist Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and the English chemist Thomas Martin Lowry stating that any compound that can transfer a proton to any other compound is an acid and the compound that accepts the proton is a base.

Bronsted Lowry Theory Definition Examples And Limitations

Bronsted Lowry Acid And Base Theory
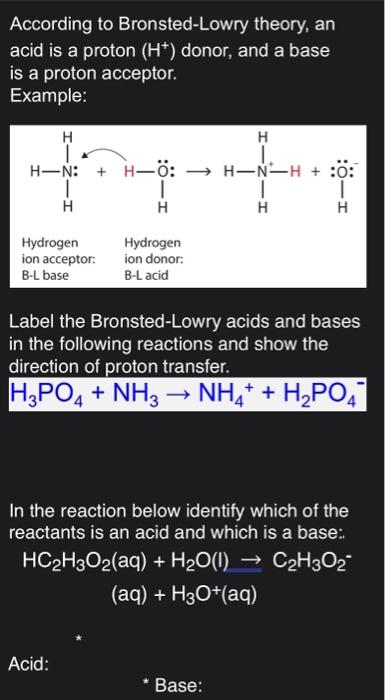
Solved According To Bronsted Lowry Theory An Acid Is A Chegg Com
0 Comments